 PDF(2721 KB)
PDF(2721 KB)


The mechanism of Danggui Buxue Decoction combined with Ginseng in improving renal interstitial fibrosis in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction by regulating the Notch signaling pathway
QIU Saiyue, TANG Lu, LUO Meixiu, PIAO Songlan, WANG Yinghang, PAN Zhi
Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2) : 128-134.
 PDF(2721 KB)
PDF(2721 KB)
 PDF(2721 KB)
PDF(2721 KB)
The mechanism of Danggui Buxue Decoction combined with Ginseng in improving renal interstitial fibrosis in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction by regulating the Notch signaling pathway
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}OBJECTIVE To investigate the mechanism of Danggui Buxue Decoction combined with Ginseng in improving renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) by regulating the Notch signaling pathway. METHODS A total of 56 Wistar rats in the specific pathogen free (SPF) level were randomly divided into sham operation (Sham) group, UUO group, losartan potassium (RX) group, Danggui Buxue Decoction (DBD) group (3.75 g·kg–1, 7.5 g·kg–1), and Danggui Buxue Decoction combined with Ginseng (GDBD) group (4.4 g·kg–1, 8.8 g·kg–1). Rats in the Sham group were stripped of the ureter without ligation, and those in the remaining groups were subjected to unilateral ureteral ligation to construct a RIF model in rats with UUO. Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr) were detected by biochemical analyzer. Serum TGF-β1, TNF-α and α-SMA in rats were detected by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining were used to observe the pathological changes and collagen fiber deposition of the kidney tissue. polymerase chain reaction(PCR) and Western blot were applied to detect the mRNA and protein levels of Notch1, JAG1 and HES1 in rat kidney tissue, respectively. RESULTS Compared with Sham group, rats in the UUO group had abnormal renal function, increased serum levels of kidney injury and fibrosis markers (TGF-β1, TNF-α, α-SMA), and upregulated mRNA and protein levels of Notch1, JAG1 and HES1. Compared with the UUO group, opposite changing trends were observed in rats with drug administration. There were significant differences in the levels of BUN, Cr, α-SMA, Notch1, JAG1 and HES1 between DBD and GDBD groups. CONCLUSION Ginseng has a synergistic effect on DBD in delaying RIF. GDBD plays an important role in delaying RIF in UUO rats by downregulating TGF-β1 and regulating the Notch signaling pathway.
Danggui Buxue Decoction / ginseng / Notch signaling pathway / unilateral ureteral obstruction / renal interstitial fibrosis {{custom_keyword}} /
Tab 1 Primers used in real-time qPCR表1 实时qPCR引物 |
| 基因 | 正向引物序列 | 反向引物序列 |
|---|---|---|
| Notch1 | 5’-TGGACCAGATTGGGGAGTTC-3’ | 5’-GCACACTCGTCTGTGTTGAC-3’ |
| JAG1 | 5’-GGGGCAACACCTTCAACCTC-3’ | 5’-CCAGGCGAAACTGAAAGGC-3’ |
| HES1 | 5’-TCAACACGACACCGGATAAAC-3’ | 5’-GCCGCGAGCTATCTTTCTTCA-3’ |
| β-actin | 5’-GTCGTACCACTGGCATTGTG-3’ | 5’-TCTCAGCTGTGGTGGTGAAG-3’ |
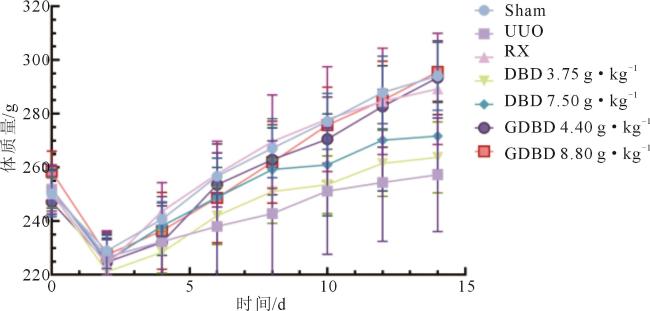
Fig 1 Effects of DBD and GDBD on body weight of UUO rats( |
Tab 2 Effects of DBD and GDBD on renal organ index and renal function indicators in UUO rats ( |
| 组别 | 脏器指数/% | BUN/ (mg·dL–1) | Cr/ (μmol·L–1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 0.32±0.03 | 17.42±0.56 | 44.33±2.41 |
| UUO | 0.56±0.02a | 34.07±0.83a | 68.02±2.77a |
| RX | 0.47±0.02b | 25.98±1.27b | 49.35±1.18b |
| DBD 3.75 g·kg–1 | 0.51±0.02c | 26.71±1.94b | 57.95±2.79b |
| DBD 7.5 g·kg–1 | 0.49±0.03b | 25.83±1.74b | 54.40±0.87b |
| GDBD 4.4 g·kg–1 | 0.49±0.02b | 24.20±0.71bd | 48.40±1.38bd |
| GDBD 8.8 g·kg–1 | 0.47±0.03b | 21.70±0.24be | 47.53±1.05be |
| 注(note):与Sham组相比(vs. Sham group),aP<0.01;与UUO组比较(vs. UUO group),bP<0.01,cP<0.05;与DBD 3.75 g·kg–1组比较(vs. DBD 3.75 g·kg–1 groups),dP<0.01;与DBD 7.5 g·kg–1组比较(vs. DBD 7.5 g·kg–1 groups),eP<0.01。 |
Tab 3 Effects of DBD and GDBD on serum TGF-β1,TNF-α and α-SMA in UUO rats ( |
| 组别 | 剂量/(g·kg–1) | TGF-β/(ng·mL–1) | TNF-α/(pg·mL–1) | α-SMA/(pg·mL–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | - | 50.89±6.46 | 232.00±11.08 | 183.61±11.98 |
| UUO | - | 90.43±10.10a | 312.56±23.51a | 256.37±17.90a |
| RX | 0.01 | 59.45±4.13b | 277.59±10.12b | 223.64±14.68b |
| DBD 3.75 g·kg–1 | 3.75 | 73.14±4.23b | 293.42±13.58 | 229.59±11.06b |
| DBD 7.5 g·kg–1 | 7.5 | 71.93±8.84b | 276.71±20.12b | 211.31±3.58b |
| GDBD 4.4 g·kg–1 | 4.4 | 69.92±4.98b | 271.02±12.93b | 203.19±7.79bd |
| GDBD 8.8 g·kg–1 | 8.8 | 61.29±3.22b | 255.84±5.32b | 201.44±2.99b |
| 注(note):与Sham组相比(vs. Sham group),aP<0.01;与UUO组比较(vs. UUO group),bP<0.01;与DBD 3.75 g·kg–1组比较(vs. DBD 3.75 g·kg–1 groups),dP<0.01。 |
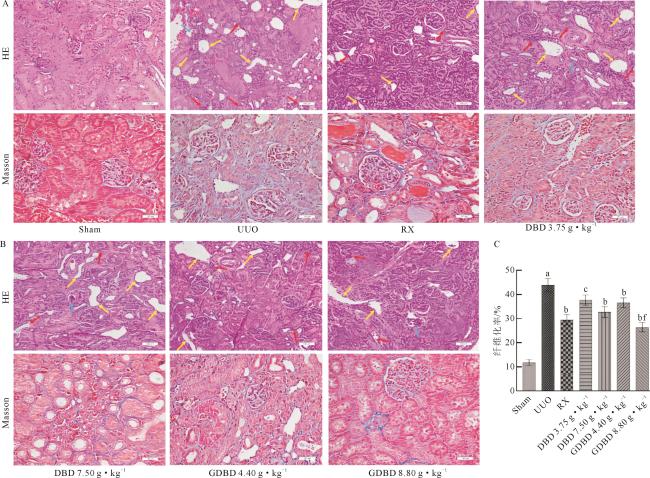
Fig 3 H&E staining (×200) and Masson’s trichrome staining (×400) of renal interstitial tissue in UUO rats treated with DBD and GDBD (A-B),and the quantification of fibrotic rate (C) ( |
Tab 4 The mRNA levels of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in rats of each group ( |
| 组别 | Notch1 | JAG1 | HES1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 0.60±0.05 | 0.66±0.03 | 0.31±0.03 |
| UUO | 1.13±0.07a | 1.27±0.05a | 0.81±0.04a |
| RX | 0.73±0.06b | 0.83±0.07b | 0.61±0.05b |
| DBD 3.75 g·kg–1 | 0.79±0.04b | 1.02±0.06b | 0.50±0.03b |
| DBD 7.5 g·kg–1 | 1.00±0.04 | 0.83±0.04b | 0.49±0.04b |
| GDBD 4.4 g·kg–1 | 0.81±0.05b | 1.05±0.06b | 0.43±0.04b |
| GDBD 8.8 g·kg–1 | 0.87±0.03b | 0.95±0.05b | 0.33±0.03be |
| 注(note):与Sham组相比(vs. Sham group),aP<0.01; 与UUO组比较(vs. UUO group),bP<0.01;与DBD 7.5 g·kg–1组比较(vs. DBD 7.5 g·kg–1 groups),eP<0.01。 |
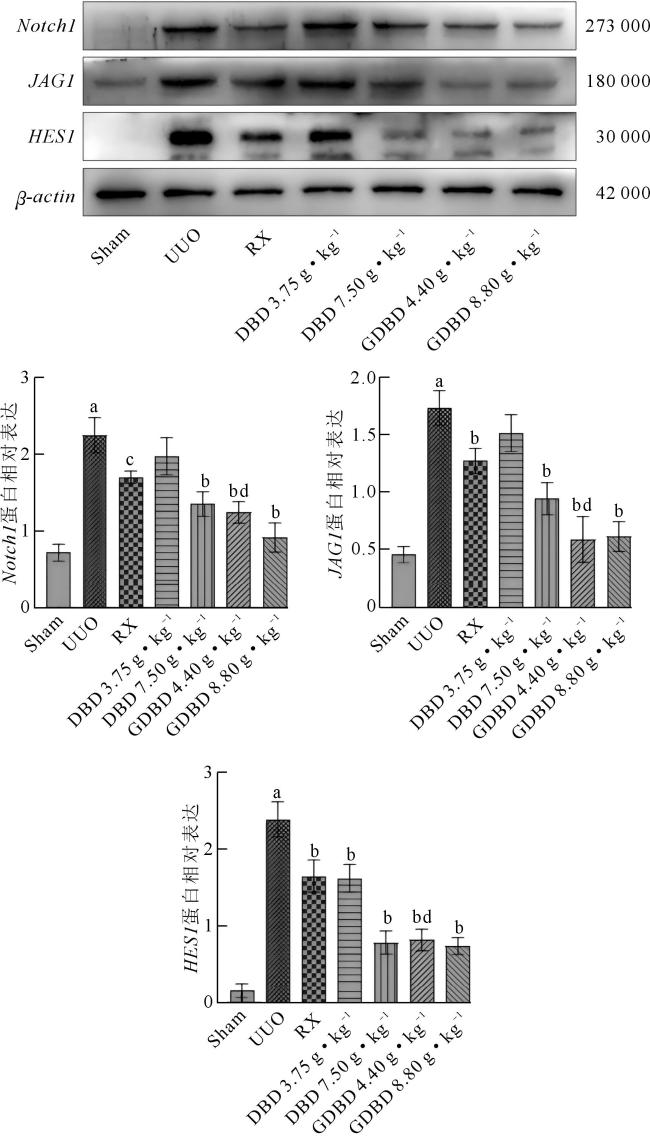
Fig 4 Protein expressions of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in contralateral kidney of UUO rats detected by Western blot ( |
| 1 |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 2 |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 3 |
张忠阳, 凌家艳, 周盾. 肾气丸对肾间质纤维化大鼠肾组织TGF-β1/Smad3信号通路及AngⅡ表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(17): 4298-4302.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 4 |
Tubular epithelial cells undergoing epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a crucial event in the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF). Bone morphogenetic protein‑7 (BMP‑7) has been reported to exhibit anti‑fibrotic functions in various renal diseases. However, the function of BMP‑7 in regulating EMT and the progression of RIF remains largely unknown. The aim of the present study was to examine the potential effect of BMP‑7 on transforming growth factor β1 (TGF‑β1)‑induced EMT and the underlying mechanisms by which BMP‑7 exerted its effects. Human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK‑2) were treated with TGF‑β1 for various time periods and at various concentrations and lentiviral vectors were used to overexpress BMP‑7. Cell Counting Kit‑8 and Transwell assays were used to evaluate the viability and migration of HK‑2 cells in vitro. EMT was estimated by assessing the changes in cell morphology and the expression of EMT markers. In addition, the activation of the Wnt3/β‑catenin and TGF‑β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathways were analyzed using western blotting. TGF‑β1 induced EMT in a time‑ and dose‑dependent manner in HK‑2 cells. Treatment with TGF‑β1 induced morphological changes, decreased cell viability and the expression of E‑cadherin, increased cell migration and the expression of α‑smooth muscle actin, fibroblast‑specific protein 1, collagen I and vimentin, and activated the Wnt3/β‑catenin and TGF‑β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathways in HK‑2 cells. However, BMP‑7 overexpression notably reversed all these effects. These results suggest that BMP‑7 effectively suppresses TGF‑β1‑induced EMT through the inhibition of the Wnt3/β‑catenin and TGF‑β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathways, highlighting a potential novel anti‑RIF strategy.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 5 |
朱玲玲, 佘云, 余江毅, 等. 中药调控糖尿病肾脏疾病肾间质纤维化相关信号通路研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30(5): 213-225.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 6 |
孙倩, 李姗姗, 杨少宁, 等. 中医药调控Notch信号通路防治肾脏疾病研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2021, 27(24): 227-234.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 7 |
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is an immune complex-mediated disease involved in the kidney disease. Recent studies have revealed that Notch signaling-related genes are aberrantly expressed in various cell types and maybe associate with inflammation-induced carcinogenesis. The aim of our study was to investigate the function of Notch1 in the inflammatory response of IgAN.The expression of Notch1, Jagged1 and NICD1 in 52 IgAN renal tissues and 20 control renal tissues was first determined using quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot. ELISA was then used to estimate the inflammatory response of human podocytes to LPS. NF-κB activity was measured using dual-luciferase reporter assay. Activation of Notch1 and NF-κB signaling pathway was assessed using Western blot.The expression of Notch1, NICD1 and Jagged1 was significantly higher in IgAN renal tissues than control renal tissues (P < 0.05). LPS treatment resulted in an obvious increase of MCP-1, IL-8 and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 in podocytes polymeric IgA (pIgA) IgAN group compared to control group (P < 0.05 for all). Activated Notch1 and its target genes, Hes1 and Hey1 were also enhanced upon LPS stimulation. Silencing of Notch1 signaling with inhibitor DAPT, NF-κB activation and LPS-induced inflammatory response were obviously attenuated, whereas Notch1 activator Jagged1 could markedly restore NF-κB activity and LPS-induced inflammatory response (P < 0.05 for all).Crosstalk between TLR4 and Notch1 signaling regulates the inflammatory response in the IgAN and maybe plays an important role in the progression of IgAN.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 8 |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 9 |
叶太生, 张莹雯, 王秀萍, 等. 当归补血汤醇提物和水提物调控BMP-7、TGF-β1表达对腺嘌呤诱导的肾间质纤维化大鼠保护作用的比较[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2018, 29(11): 2619-2622.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 10 |
倪赛宏, 傅水莲, 何丽明, 等. 人参皂苷在肾脏疾病中的药理作用研究进展[J]. 人参研究, 2018, 30(2): 37-40.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 11 |
张春晶, 张越, 王小龙, 等. 人参皂苷Rh1对UUO大鼠肾纤维化的抑制作用[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2018, 34(12): 2289-2293.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 12 |
吕鹏, 侯丽, 赵欢, 等. 龙贝逍遥散冻干粉对人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7增殖、迁移及p53、c-Myc及caspase-3表达的影响[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2020, 15(1): 1-4, 8.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 13 |
刘洋, 张瑞红, 只素娟, 等. 肾纤维化手术动物模型构建及相关机制研究进展[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2022, 45(2): 157-160.
The progression of various chronic kidney disease to a certain stage leads to renal fibrosis. Renal fibrosiscan be stimulated by a variety of factors, including kidney trauma, infection, blood circulation blockage or immuneresponse, etc. After renal tissue damage caused by these factors, a large number of collagen fibers deposited inthe stroma to form fibrous scars, which resulted in changes of renal structure and function and further led to renalfibrosis. So far, the mechanism of renal fibrosis remains not fully understood. The establishment of an ideal animalmodel is of great significance for the study of the mechanism of renal fibrosis. Numerous literatures reported theestablishment of animal models of renal fibrosis through surgery. Therefore, this article focused on the methods ofestablishment of animal model of renal fibrosis by sur gery and the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis in recent years.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 14 |
代云莉, 彭灿, 梁丹, 等. 氧化苦参碱减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠肾组织炎症及纤维化反应的机制研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2024, 34(6): 31-37.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 15 |
蒲金赟, 周建华. 槐杞黄清膏抑制UUO大鼠肾间质纤维化的初步研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2015, 35(13): 1199-1204.
<p><strong>OBJECTIVE </strong>To design this experiments to evaluate therapeutic effects of Chinese herbal medicine Huaiqihuang(HQH) on obstructive kidneys and explore the involved mechanism.<strong>METHODS </strong>Wistar rats were randomly assigned to five groups, 5 rats in each group. Rats in control groups received sham operation and normal saline. Rats in model groups and treatment groups were intragastrically administrated normal saline and different doses of Huaiqihuang (Low-dose 1.5 g·kg<sup>-1</sup>, Mid-dose 2.25 g·kg<sup>-1</sup>, High-dose 3.0 g·kg<sup>-1</sup>) respectively from D3 after left ureter ligation. Protein expressions of ɑ-SMA in obstructive kidneys were analyzed by IHC and western blots. <strong>RESULTS </strong>After rats were sacrificed on D14, histopathological changes were observed, UUO rats on D14 showed significant tubulointerstitial lesions with severe fibrosis. Clusters of myofibroblasts appeared in renal institium. Mid-dose and High-dose rather than low-dose treated rats showed lesions and fibrosis of mild degrees. The study revealed that both Mid-dose and High-dose significantly decreased accumulation of myofibroblasts in renal institium and reduced ɑ-SMA protein expression. <strong>CONCLUSION </strong>2.25 g·kg<sup>-1</sup> and 3.0 g·kg<sup>-1</sup> HQH at early stage of renal fibrosis can effectively attenuate renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting accumulation of myofibroblasts.</p>
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 16 |
高琛妮, 沈平雁, 潘召城, 等. 腹膜后纤维化7例的临床特点和治疗方案分析[J]. 上海医学, 2017, 40(1): 41-44.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 17 |
任荣, 张静, 张蕾. 腹膜透析与血液透析对尿毒症患者钙磷代谢、炎症细胞因子及肾纤维化指标的影响比较[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2021, 22(10): 900-902.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 18 |
杨茹茜, 王雪. 黄芪及其制剂基于信号通路机制抗肾纤维化的研究概况[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(6): 3023-3026.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 19 |
郭双岩, 梁旗, 吕洁丽, 等. 中药当归的药理作用及机制研究进展[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2023, 40(7): 678-685.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 20 |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 21 |
闵亚丽, 蒋文勇, 蓝天座, 等. 红景天在肾间质纤维化大鼠模型中的作用及对CTGF、PDGF-B表达的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2012, 32(15): 1172-1175.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 22 |
杨晓萍, 张焕巧, 赵瑾, 等. 整合素连接激酶和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达与肾间质纤维化关系的研究[J]. 北京医学, 2007(10): 600-603.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 23 |
王旸, 刘娜, 王立范, 等. 薯蓣皂苷对UUO小鼠肾脏病理变化和TNF-α表达的影响[J]. 中国中医药科技, 2023, 30(2): 228-231.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| 24 |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(2721 KB)
PDF(2721 KB)
 Tab 1 Primers used in real-time qPCR
Tab 1 Primers used in real-time qPCR Fig 1 Effects of DBD and GDBD on body weight of UUO rats(
Fig 1 Effects of DBD and GDBD on body weight of UUO rats( Tab 2 Effects of DBD and GDBD on renal organ index and renal function indicators in UUO rats (
Tab 2 Effects of DBD and GDBD on renal organ index and renal function indicators in UUO rats ( Tab 3 Effects of DBD and GDBD on serum TGF-β1,TNF-α and α-SMA in UUO rats (
Tab 3 Effects of DBD and GDBD on serum TGF-β1,TNF-α and α-SMA in UUO rats ( Fig 2 Effects of DBD and GDBD on renal morphology of UUO rats
Fig 2 Effects of DBD and GDBD on renal morphology of UUO rats Fig 3 H&E staining (×200) and Masson’s trichrome staining (×400) of renal interstitial tissue in UUO rats treated with DBD and GDBD (A-B),and the quantification of fibrotic rate (C) (
Fig 3 H&E staining (×200) and Masson’s trichrome staining (×400) of renal interstitial tissue in UUO rats treated with DBD and GDBD (A-B),and the quantification of fibrotic rate (C) ( Tab 4 The mRNA levels of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in rats of each group (
Tab 4 The mRNA levels of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in rats of each group ( Fig 4 Protein expressions of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in contralateral kidney of UUO rats detected by Western blot (
Fig 4 Protein expressions of Notch1,JAG1 and HES1 in contralateral kidney of UUO rats detected by Western blot (/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |